安裝SWIG
並檢視下列檔案:
CDemo.exe
CDemo.c
安裝工具 :
除了英文的資料,另外還讀了一下關於SWIG的相關中文資料:
1.Python的資料庫形式
https://read01.com/PnGeDg.html
2.Python在Windows中用SWIG呼叫C/C++的函式(VC)
http://falldog7.blogspot.tw/2013/07/python-swig-c-function.html
3.SWIG概念
http://user.frdm.info/ckhung/b/mi/swig.php
接著從swig.org下載最新版的SWIG 3.0.10,將壓縮包解至W:內。
SWIG能夠給Windows/Unix/MacOSX三個平台使用,所以壓縮檔的附檔名是三個平台都共通的".tar.gz"。
解壓縮後,在Windows環境中有很多檔案是打不開的,不過說明檔是沒有附檔名的,隨便用任何一款文字編輯軟體都能查看。
如果該步驟需要完整的流程,\Doc\Manual中有寫好的html網頁手冊,用網頁瀏覽器就能開啟。
在閱讀\Doc\Manual\Windows.html的說明之後,手冊解釋SWIG並不是使用通常的Windows類型安裝程式。
只要在編譯器中(手冊的範例是Visual Studio)設置環境變數就能使用其範例檔。
手冊上也有說明能夠用MinGW和MSYS,Build出SWIG的可執行檔swig.exe。
CDemo.exe :
CDemo.exe是由CDemo.c編譯出來的可執行檔,取用libslvs.dll的動態連結庫運作。
在原本的\exposed資料夾中還有工程師留下的VbDemo.vb,Visual Basic或是Visual C#的專案文件,不過不使用這兩個編譯器的話就用不到。
為此特別將CDemo.exe和libslvs.dll拿出來放在獨立的資料夾中。
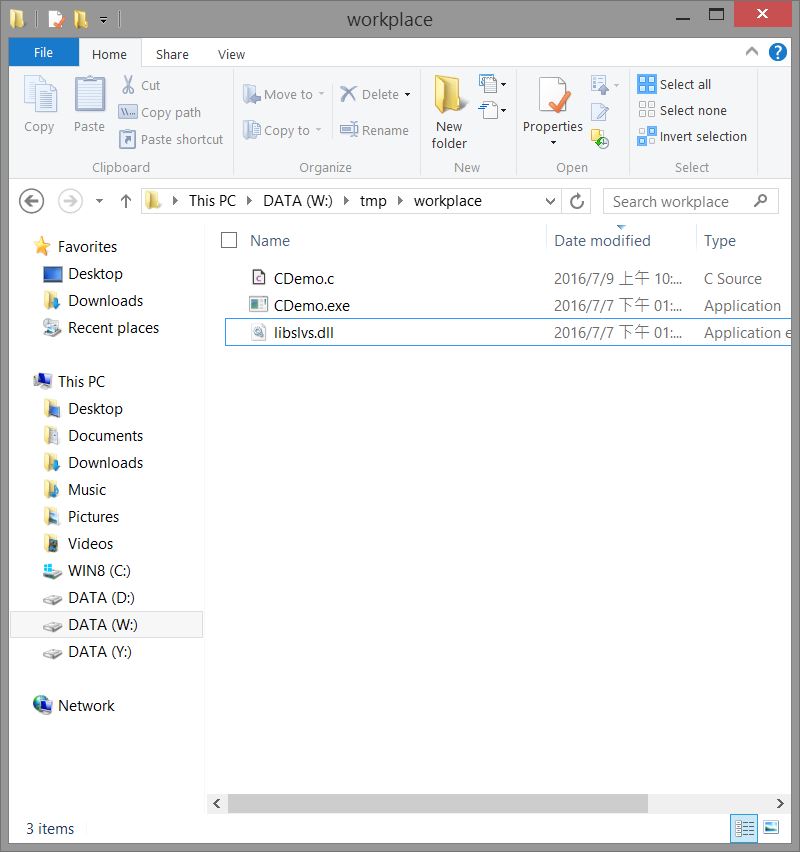
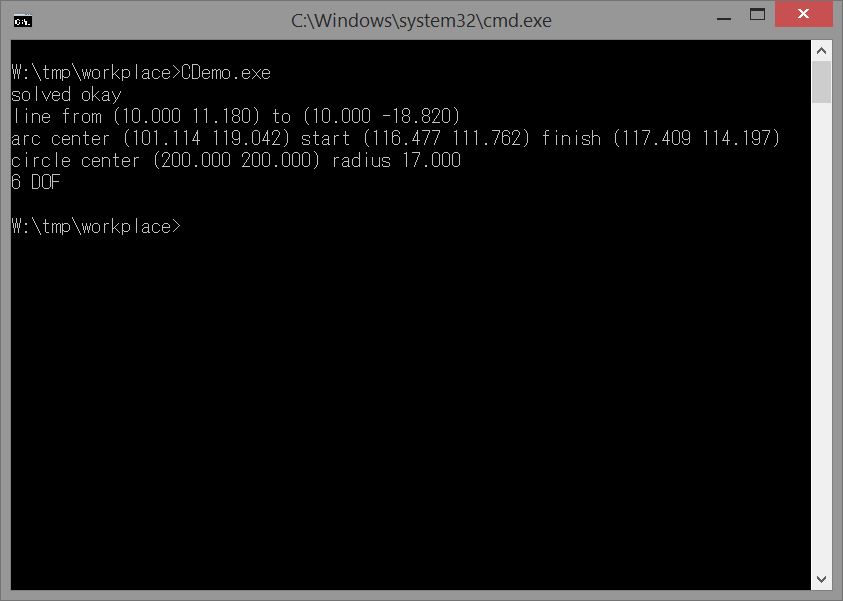
由CMD進入資料夾中執行CDemo.exe,會發現CDemo是直接顯示了結果。
顯然CDemo.exe原先已經設定好題目,於是打開CDemo.c看看工程師的註解怎麼說。
CDemo.c :
由於NetBeans和Windows的截圖程式似乎有衝突,會常常截完圖後自動閃退,所以改用簡便的SciTE。
用SciTE開啟CDemo.c,可以發現CDemo的原始碼。
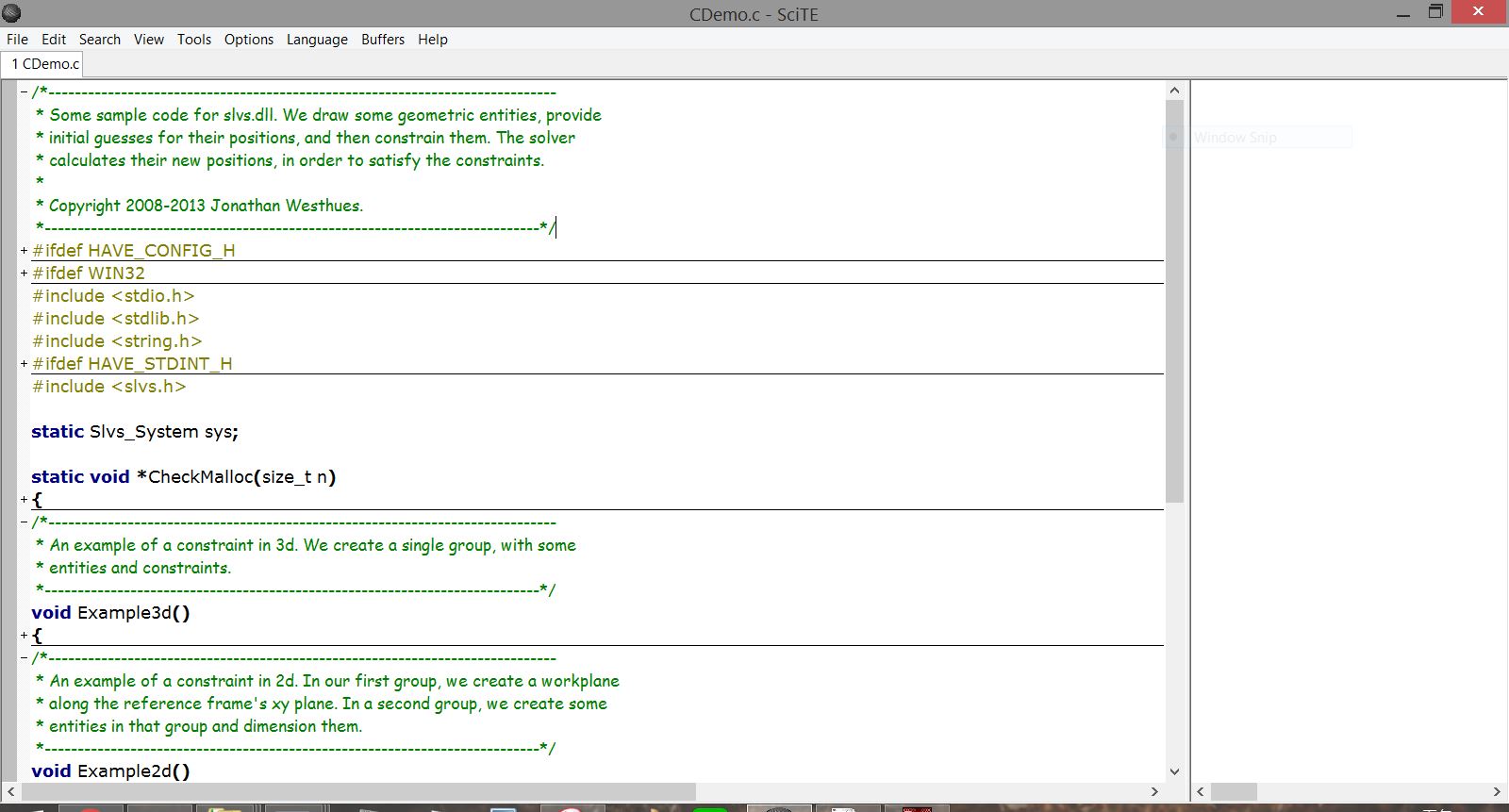
而為了方便,將它部分的原始碼貼在下面:
/*--------------------------- * Some sample code for slvs.dll. We draw some geometric entities, provide * initial guesses for their positions, and then constrain them. The solver * calculates their new positions, in order to satisfy the constraints. * * Copyright 2008-2013 Jonathan Westhues. *-------------------------*/ #ifdef HAVE_CONFIG_H ... #endif #ifdef WIN32 ... #endif #include#include #include #ifdef HAVE_STDINT_H ... #endif #include static Slvs_System sys; static void *CheckMalloc(size_t n) { void *r = malloc(n); if(!r) { printf("out of memory!\n"); exit(-1); } return r; } /*--------------------------- * An example of a constraint in 3d. We create a single group, with some * entities and constraints. *-------------------------*/ void Example3d() { ... } /*--------------------------- * An example of a constraint in 2d. In our first group, we create a workplane * along the reference frame's xy plane. In a second group, we create some * entities in that group and dimension them. *-------------------------*/ void Example2d() { ... } int main() { sys.param = CheckMalloc(50*sizeof(sys.param[0])); sys.entity = CheckMalloc(50*sizeof(sys.entity[0])); sys.constraint = CheckMalloc(50*sizeof(sys.constraint[0])); sys.failed = CheckMalloc(50*sizeof(sys.failed[0])); sys.faileds = 50; /*Example3d();*/ for(;;) { Example2d(); sys.params = sys.constraints = sys.entities = 0; break; } return 0; }
在CDemo.c的主程式中,最後執行Example3d()副程式的部分被註解掉了。
所以程式的運行主要是跑Example2d(),就把它的程式碼抓出來看一下。
void Example2d()
{
Slvs_hGroup g;
double qw, qx, qy, qz;
g = 1;
/* First, we create our workplane. Its origin corresponds to the origin
* of our base frame (x y z) = (0 0 0) */
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(1, g, 0.0);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(2, g, 0.0);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(3, g, 0.0);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakePoint3d(101, g, 1, 2, 3);
/* and it is parallel to the xy plane, so it has basis vectors (1 0 0)
* and (0 1 0). */
Slvs_MakeQuaternion(1, 0, 0,
0, 1, 0, &qw, &qx, &qy, &qz);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(4, g, qw);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(5, g, qx);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(6, g, qy);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(7, g, qz);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakeNormal3d(102, g, 4, 5, 6, 7);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakeWorkplane(200, g, 101, 102);
/* Now create a second group. We'll solve group 2, while leaving group 1
* constant; so the workplane that we've created will be locked down,
* and the solver can't move it. */
g = 2;
/* These points are represented by their coordinates (u v) within the
* workplane, so they need only two parameters each. */
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(11, g, 10.0);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(12, g, 20.0);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakePoint2d(301, g, 200, 11, 12);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(13, g, 20.0);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(14, g, 10.0);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakePoint2d(302, g, 200, 13, 14);
/* And we create a line segment with those endpoints. */
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakeLineSegment(400, g,
200, 301, 302);
/* Now three more points. */
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(15, g, 100.0);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(16, g, 120.0);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakePoint2d(303, g, 200, 15, 16);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(17, g, 120.0);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(18, g, 110.0);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakePoint2d(304, g, 200, 17, 18);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(19, g, 115.0);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(20, g, 115.0);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakePoint2d(305, g, 200, 19, 20);
/* And arc, centered at point 303, starting at point 304, ending at
* point 305. */
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakeArcOfCircle(401, g, 200, 102,
303, 304, 305);
/* Now one more point, and a distance */
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(21, g, 200.0);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(22, g, 200.0);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakePoint2d(306, g, 200, 21, 22);
sys.param[sys.params++] = Slvs_MakeParam(23, g, 30.0);
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakeDistance(307, g, 200, 23);
/* And a complete circle, centered at point 306 with radius equal to
* distance 307. The normal is 102, the same as our workplane. */
sys.entity[sys.entities++] = Slvs_MakeCircle(402, g, 200,
306, 102, 307);
/* The length of our line segment is 30.0 units. */
sys.constraint[sys.constraints++] = Slvs_MakeConstraint(
1, g,
SLVS_C_PT_PT_DISTANCE,
200,
30.0,
301, 302, 0, 0);
/* And the distance from our line segment to the origin is 10.0 units. */
sys.constraint[sys.constraints++] = Slvs_MakeConstraint(
2, g,
SLVS_C_PT_LINE_DISTANCE,
200,
10.0,
101, 0, 400, 0);
/* And the line segment is vertical. */
sys.constraint[sys.constraints++] = Slvs_MakeConstraint(
3, g,
SLVS_C_VERTICAL,
200,
0.0,
0, 0, 400, 0);
/* And the distance from one endpoint to the origin is 15.0 units. */
sys.constraint[sys.constraints++] = Slvs_MakeConstraint(
4, g,
SLVS_C_PT_PT_DISTANCE,
200,
15.0,
301, 101, 0, 0);
#if 0
/* And same for the other endpoint; so if you add this constraint then
* the sketch is overconstrained and will signal an error. */
sys.constraint[sys.constraints++] = Slvs_MakeConstraint(
5, g,
SLVS_C_PT_PT_DISTANCE,
200,
18.0,
302, 101, 0, 0);
#endif /* 0 */
/* The arc and the circle have equal radius. */
sys.constraint[sys.constraints++] = Slvs_MakeConstraint(
6, g,
SLVS_C_EQUAL_RADIUS,
200,
0.0,
0, 0, 401, 402);
/* The arc has radius 17.0 units. */
sys.constraint[sys.constraints++] = Slvs_MakeConstraint(
7, g,
SLVS_C_DIAMETER,
200,
17.0*2,
0, 0, 401, 0);
/* If the solver fails, then ask it to report which constraints caused
* the problem. */
sys.calculateFaileds = 1;
/* And solve. */
Slvs_Solve(&sys, g);
if(sys.result == SLVS_RESULT_OKAY) {
printf("solved okay\n");
printf("line from (%.3f %.3f) to (%.3f %.3f)\n",
sys.param[7].val, sys.param[8].val,
sys.param[9].val, sys.param[10].val);
printf("arc center (%.3f %.3f) start (%.3f %.3f) finish (%.3f %.3f)\n",
sys.param[11].val, sys.param[12].val,
sys.param[13].val, sys.param[14].val,
sys.param[15].val, sys.param[16].val);
printf("circle center (%.3f %.3f) radius %.3f\n",
sys.param[17].val, sys.param[18].val,
sys.param[19].val);
printf("%d DOF\n", sys.dof);
} else {
int i;
printf("solve failed: problematic constraints are:");
for(i = 0; i < sys.faileds; i++) {
printf(" %d", sys.failed[i]);
}
printf("\n");
if(sys.result == SLVS_RESULT_INCONSISTENT) {
printf("system inconsistent\n");
} else {
printf("system nonconvergent\n");
}
}
}
"Slvs_hGroup g"中的g能在群組編號中切換,離開後的群組會被鎖定。裡面的成員無法新增和編輯,不過可以被呼叫。
之後便能用"sys.param[sys.params++]"或是"sys.entity[sys.entities++]"的指令在群組下建立工作物件(回傳值,物件格式是%.3f)和建立實體(檢查結果)。
比較特別的是本程式建立座標的編號是從1開始的;建立工作點的編號是從101開始的;建立工作平面是從200開始的(這題只有一個工作平面);建立點的編號是從301開始的(使用的座標和工作點相同層級)。之後層級越高編號都以100的倍數成長。
畫完圖之後,最後解決的程式是使用Slvs_Solve(&sys, g);,取得程式結果和輸入群組編號。至於這個範疇就是libslvs.dll和其他Solvespace部件的工作了。
閱讀完pyd檔案的作用後,大約知道它和dll的關聯性了。
不過libslvs.dll究竟是從哪裡編譯出來的呢?是從主要的cpp檔還是標頭檔建立的?Build完之後多出了libslvs.dll.a和config.h。
雖然一些簡單的dll可以直接打開編輯,不過libslvs.dll應該是不能這樣做。
Comments
comments powered by Disqus